Sep 11th 2025
Most common technologies to monitor water pipeline leakage
Most common technologies to monitor water pipeline leakage
Infrastructure Monitoring is the Backbone of Modern Water Utilities. Water utilities around the world are under immense pressure to deliver safe, reliable, and sustainable water supply while managing aging infrastructure and increasing demand and one of the key questions we received from our clients is: "What is the best technology to monitor water pipeline leakage"

10sorex pipeline pressure monitoring for leak detection
In California and beyond, decades-old pipelines, valves, and reservoirs form the backbone of distribution networks—many of which were never designed to support today’s population size, environmental stress, or real-time data expectations. As droughts intensify and resources tighten, the ability to continuously monitor system performance has moved from optional to essential.
Aging infrastructure isn't just a reliability issue—it’s a cost sink. According to the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA), water loss due to leaks accounts for 20–30% of total supply in many utilities. The American Water Works Association estimates that one mile of leaking pipe can waste over 100,000 gallons of water per day, and the cost of reactive repairs is 4-7x higher than proactive maintenance driven by sensor data. The result? Millions in annual losses, service interruptions, regulatory fines, and frustrated ratepayers.
Leak detection is the linchpin of infrastructure health. Early detection not only prevents major bursts and road collapses, but also improves asset lifespan, protects water quality, and ensures more equitable service delivery. However, detecting leaks—especially in large or buried pipe networks—is not straightforward. No single technology provides a universal solution. Each method, from acoustic sensors to satellite imagery to LPWAN pressure monitoring, has specific strengths and limitations depending on pipe material, location, flow rate, and environmental factors.
That’s the core challenge for utilities: choosing the right mix of tools. Smart infrastructure monitoring isn’t about deploying one perfect solution. It’s about building a layered, cost-effective approach that aligns with system complexity and operational goals. In this article, in a very high level, we break down the most widely used leak detection techniques—how they work, where they shine, and where they fall short—so utilities can build a strategy based on real data, not guesswork.
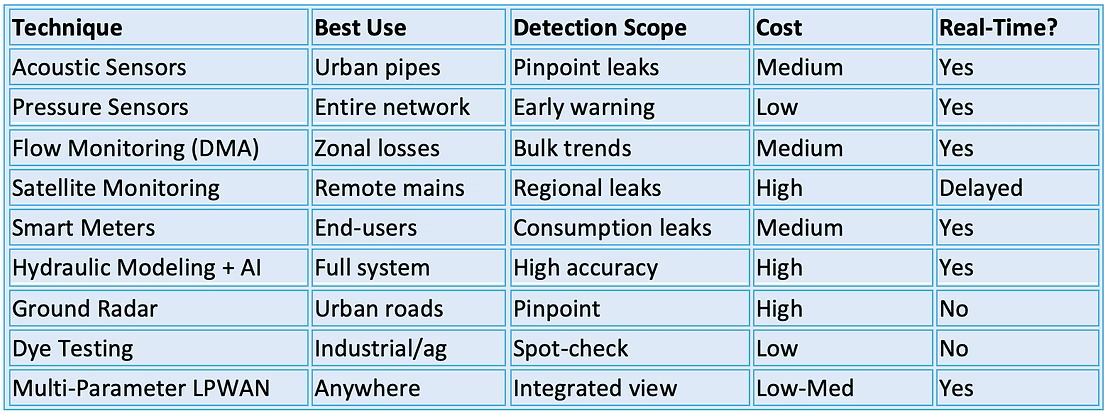
Monitoring water leakage effectively—especially in large-scale water utilities or distribution networks—requires a combination of sensing technologies, analytical models, and communication infrastructure. Here are the key techniques used today:
different technologies to detect the leak in water pipelines
- Acoustic Leak Detection
- How it works: Uses sensitive microphones or hydrophones to pick up sound waves generated by water escaping under pressure from a pipe.
- Best for: Metal pipes and high-pressure systems.
- Common tools: Ground microphones, correlators, and geophones.
- Pros: Non-invasive, real-time pinpointing.
- Limitations: Less effective in plastic pipes or noisy environments. high cost
- Pressure Monitoring and Pressure Transients
- How it works: Continuously monitors pressure in pipelines. Sudden drops or abnormal fluctuations can indicate leakage or burst.
- Advanced version: Transient-based methodsdetect pressure drop caused by leakage events.
Technologies: LoRaWAN / NB-IoT pressure sensors like 10sorex PTS3 / PTD2. - Pros: Affordable, scalable, real-time alerts.
- Best use: Distributed monitoring in both urban and rural zones. sometimes doesn't work accurately for a very early leak phase.
- Flow Monitoring and District Metered Areas (DMAs)
- How it works: Water networks are divided into zones (DMAs), and flow meters are used to monitor input and output. Any discrepancies indicate non-revenue water (leaks or theft).
- Technique: Minimum Night Flow analysisis commonly used to isolate leakage from usage.
- Pros: Effective at identifying zones with losses.
- Limitation: Doesn’t pinpoint exact leak location.
- Satellite-Based Remote Sensing
- How it works: Measures soil moisture anomalies from space to detect underground water leaks.
- Used by: Some utilities in Europe, Middle East, and Asia for major transmission pipelines.
- Pros: Covers large areas quickly.
- Cons: Not suitable for small leaks or urban areas with high surface variation.
- Smart Water Meters with Consumption Analytics
- How it works: Smart meters track usage in near real time. Abnormal consumption trends (e.g., continuous flow overnight) can suggest a leak.
- Advanced analytics: AI and ML can classify patterns indicative of specific leak types (drip, burst, etc.).
- Pros: Great for residential/commercial end-point leak detection.
- Used in: Smart cities, water conservation programs.
- Hydraulic Modeling and AI-Based Leak Detection
-
- How it works: Models simulate expected pressure/flow under normal operation. Deviations are matched to potential leak signatures using AI.
- Integrates: Pressure, flow, valve state, sensor data.
- Pros: Detects both real leaks and system inefficiencies.
- Used in: Larger utilities with digital twins or advanced SCADA platforms.
- Ground Penetrating Radar (GPR) / Infrared Thermography
- How it works: Detects changes in subsurface conditions or thermal differences caused by leaking water.
- Used for: Pinpointing difficult leaks under roads or concrete.
- Pros: High accuracy.
- Cons: Expensive and requires trained operatorsx
- Dye or Chemical Tracing
- How it works: Introduces harmless dye or tracer chemical into the pipe. Leakage points are identified by detecting the substance downstream or in the soil.
- Used in: Old industrial or irrigation systems.
- Pros: Precise leak detection.
- Cons: Manual process; not scalable.
- Integrated Multi-Sensor Nodes (Pressure + Flow + Water Quality)
- Modern solution, combines collected data from different sensors:
- Connectivity: LoRaWAN or NB-IoT or Satellite
- Advantages: Full-picture diagnostics with low power and low-cost deployment.
At 10sorex, we are proud of supporting many water utilities across the globe with our advanced technologies to monitor pipelines and other critical assets to save the most precious asset gifted to us.
